If you have been working in the IT industry for quite some time, it is safe to assume you have come across the concept of dedicated static IPs and rotating shared IPs at least once. Chances are they might have puzzled you to a certain degree, especially if your company is thinking about leasing IPs to scale its business. After all, there are different types of IPs, so branching them into IPv4 and IPv6 is sometimes not enough. Let’s see what’s the difference between dedicated static and rotating shared IPs and find the answers to the most important questions that will help you to choose the best option.
You saw the title of this article and decided to click on it. Now, unless you did that by mistake, it means you are at least familiar with the basic concepts of IPs. But for the sake of completeness, let’s briefly discuss what’s an IP. To put it simply, an IP address helps identify a device connected to the Internet.
You can think of it just like you would think of sharing your home address in order to receive a delivery. To put it even simpler and more ridiculous, an IP is… the street number where your computer lives! There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. They serve the same purpose, but have different characteristics. Which brings us to the idea of dedicated static IPs and rotating shared IPs.
What are rotating shared IPs?
When you rotate an IP you actually assign an IP address to a device at random or scheduled intervals. Let’s discuss an example. When your Internet Service Provider (ISP) provides you with an active Internet connection, an IP address is picked from a pool of IPs and is automatically allocated to your system. When you disconnect from or connect to the Internet, the ISP will allocate your system the next available IP address.
Basically, whenever a user disconnects from the Internet, the ISP will take that particular user’s IP address back to the original IP address pool. You might wonder why this is a thing. Well, this process is highly efficient in optimizing the existing resources.
Rotating IP addresses is not practiced exclusively by ISPs. Many Internet users across the world actually rotate their IP addresses intentionally, since this can have a couple of benefits. In fact, these users rotate proxies, which in turn helps them benefit from multiple IP addresses. There are different methods of rotating IP addresses, but generally speaking, if you accurately configure the proxy server, numerous connections from a single device can be set up and managed.
What can you do with rotating shared IPs?
The aforementioned advantages rely upon task automatization for, let’s say, data scraping and web crawling operations, for greater efficiency and success rate. Furthermore, web crawling is a particularly tricky process, prone to being blacklisted, flagged, or banned by websites while trying to gather the data. If you use rotating shared IPs, you can significantly avoid these risks while gathering huge amounts of data.
In addition, SEO firms opt for rotating shared IPs either to verify keyword rankings in various locations/countries or to promote specific content on social media platforms. And last but not least, data intelligence companies are “fond” of this method when scraping websites for analytics and/or for checking performance.
Now that we’ve covered the idea of rotating shared IP addresses, let’s discuss their counterpart: dedicated static IPs.
What are dedicated static IPs?
As the name implies, a dedicated static IP address is a single address assigned to a single owner. More specifically, it is the unique identifying address of that particular domain on the Web. It is individual to you and your company, utilizing a dedicated server that handles your traffic only.
It’s interesting to note that it might seem counterintuitive to assign dedicated static IP addresses to specific users in times like these, when more and more devices connect to the Internet and the IPv4 addresses are becoming scarcer and scarcer.
However, a dedicated static IP can bring many benefits to the user, inasmuch as more and more companies tend to opt for such addresses. Tackling IPv4 scarcity is a tough job, but the benefits of companies using dedicated addresses cannot be overstated. Let’s have a look at some of the most common and important examples.
What can you do with dedicated static IP addresses?
Dedicated static IPs often prove themselves very useful for many companies and businesses. In some scenarios, they can be even indispensable!
You can test them before putting them into production to see if they provide access to your desired website
Once you acquire or lease the number of IP addresses you want, you can actually test them to check if they work properly i.e if they can be used to access the websites you want. It is an important advantage that companies might want to leverage. It also helps users connect to their hosting accounts no matter where they are and ensure a quicker transfer speed of large amounts of data.
You can consolidate the control of your server
Having a dedicated static IP address greatly expands use cases. This expansion is the result of the improved server control that is ensured by using dedicated IPs. This combination allows companies to do many things, such as running a VPN, managing their servers remotely, and handling their data more efficiently.
Increased email deliverability
If your business revolves around email marketing, you should know that dedicated static IP addresses reduce the risk of issues associated with email deliverability. Mail servers are highly IP sensitive, and you will often have to deal with blacklisted IPs. Dedicated addresses mitigate this risk and increase spam avoidance.
Let’s put it like this: if one hosting account you share an IP address with starts sending spam, you risk getting all your sent mails blocked as well. This is why such businesses will almost always choose to invest in a pool of dedicated IP addresses.
What are the main differences between rotating shared IPs and static dedicated IPs?
Hopefully by now you have understood how dedicated static and rotating shared IPs generally work. All in all, each type has its own characteristics. At the end of the day, it is up to the respective companies to opt for the type that suits their needs best. As a final disposition, let’s sum up the most important differences between dedicated static and rotating shared IPs.
You can check a quick infographic down below. Compressed, well-structured and easy to understand, it contains everything you need to know about key differences and use cases.
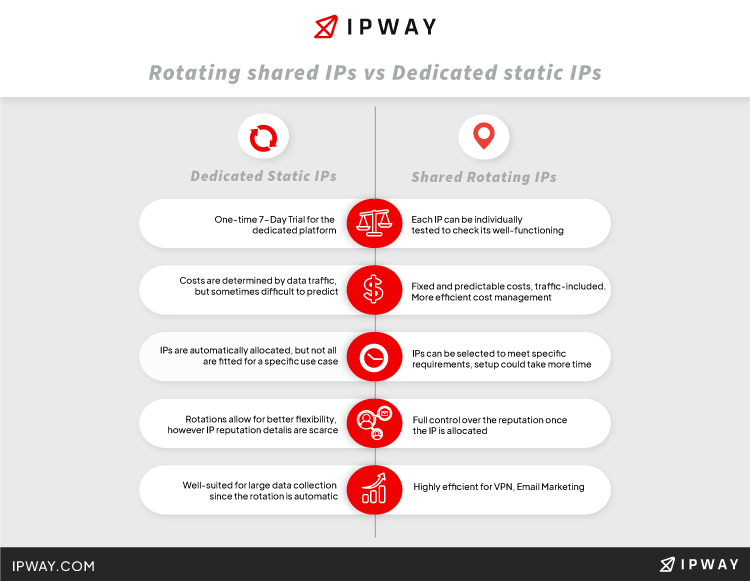
When it comes to dedicated static IP addresses, clients can verify them for faulty performance. They have 24 hours to test the IPs in any environment i.e databases, websites, before deciding to purchase them. Furthermore, since they are static, once clients acquire them, the addresses are theirs to own and carefully manage.
Shared IPs can be a bit tricky to handle, given the fact that rotating them is a complex and sometimes tedious operation. Nevertheless, they equally provide benefits, should a company decide to invest in such a service.
It’s up to the client to manage and customize their dedicated static IP address pool. Hence the aforementioned idea of owning your own address pool. This can be quite advantageous because acquiring such fresh IPs means access to websites of interest will never be blocked “out of the box”.
Such a guarantee is not that valid when it comes to rotating shared IP addresses, so you should bear in mind this small detail when deciding to rotate IPs. Think of it like borrowing a book or a video game console from someone. The book might look and feel used, the writing on the pages might look faded and unreadable, just as the console might have some app lock set up by its original owner, thus making it a bit clumsy. However, in either case, the use cases and flexibility remain noteworthy. (some sites can be blocked)
It is important to stress the difference between costs as well if you want to make an informed decision. Depending on which type of IP you choose, monthly pricing needs to be taken into consideration. Owning a dedicated static IP address means a fixed fee, with an easily predictable monthly cost. This means you won’t be charged for the traffic associated with that address.
Compared to that, using rotating shared IPs always implies bandwidth costs that can be difficult to forecast or assimilate into a company’s budget. In most cases, your allocated traffic will be less than what dedicated static IPs offer. The latter seems to be more convenient for enterprises that require massive amounts of bandwidth without concern regarding additional costs.
That being said, dedicated static IPs and their rotating shared counterparts are equally useful, but outline some important differences. Needless to say, IP addresses have become a valuable commodity for many enterprises, and it’s important to make sure that your company benefits the most, no matter what service you opt for.
When making an informed choice companies can conserve their financial resources and spend them wisely on more important assets. Thus, IPs become an important aspect for a company’s expenditures, which need to be smartly dealt with.
